
Projects
A selected collection of my projects.
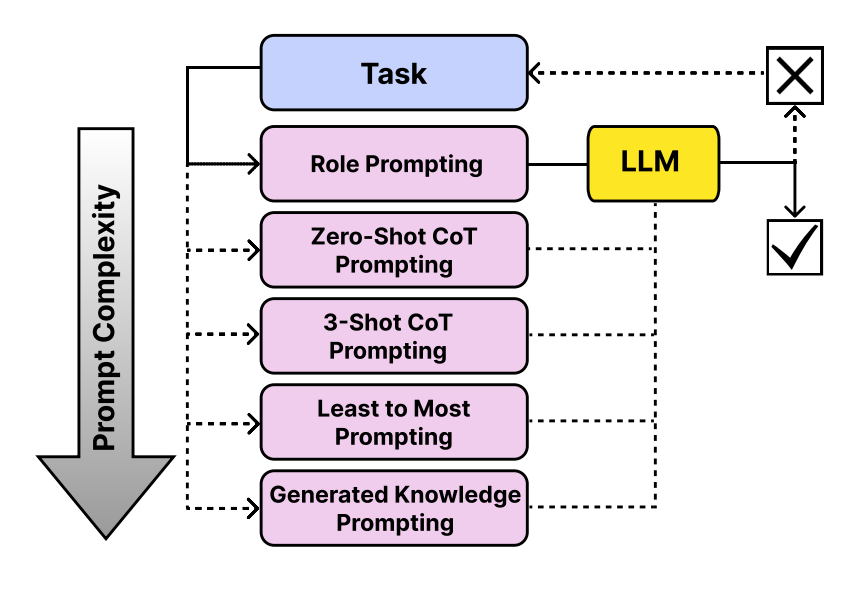
Hierarchical Prompting Taxonomy (HPT)
HPT is a cognitively motivated evaluation framework for large language models that categorizes prompting strategies by their cognitive demands and introduces the Hierarchical Prompting Index (HPI) to quantify task complexity. The framework enables systematic analysis of reasoning capabilities across datasets and models, yielding consistent performance improvements and interpretable insights into LLM problem-solving behavior.
Hierarchical Prompting Taxonomy: A Universal Evaluation Framework for Large Language Models Aligned with Human Cognitive Principles
Devichand Budagam, Ashutosh Kumar, Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Sankalp KJ, Vinija Jain, Aman Chadha
KDD workshop on Prompt Optimization 2025
Hierarchical Prompting Taxonomy: A Universal Evaluation Framework for Large Language Models Aligned with Human Cognitive Principles
Devichand Budagam, Ashutosh Kumar, Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Sankalp KJ, Vinija Jain, Aman Chadha
KDD workshop on Prompt Optimization 2025

T2IScoreScore
Our research expands on recent progress in Text-to-Image (T2I) models, concentrating on enhancing image generation quality. Despite advancements, challenges like hallucination persist. Automated T2I metrics aim to monitor progress, yet their blindspots, rooted in training on natural images, result in inconsistent scoring for images that are semantically equivalent.
We introduce T2IScoreScore, a curated dataset that systematically transitions images from high to low faithfulness. This dataset includes synthetic and natural examples, providing a foundation for a comprehensive "meta-evaluation" of existing T2I metrics. By directly addressing blindspots, our work contributes to refining T2I models, aiming to reduce object hallucination and improve image consistency. The ultimate goal is to enhance the models' proficiency in aligning with textual descriptions.
Who Evaluates the Evaluations? Objectively Scoring Text-to-Image Prompt Coherence Metrics with T2IScore (TS2)
Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Michael Saxon, Fatima Jahara, Yujie Lu, Aditya Sharma, William Yang Wang
NeurIPS 2024
We introduce T2IScoreScore, a curated dataset that systematically transitions images from high to low faithfulness. This dataset includes synthetic and natural examples, providing a foundation for a comprehensive "meta-evaluation" of existing T2I metrics. By directly addressing blindspots, our work contributes to refining T2I models, aiming to reduce object hallucination and improve image consistency. The ultimate goal is to enhance the models' proficiency in aligning with textual descriptions.
Who Evaluates the Evaluations? Objectively Scoring Text-to-Image Prompt Coherence Metrics with T2IScore (TS2)
Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Michael Saxon, Fatima Jahara, Yujie Lu, Aditya Sharma, William Yang Wang
NeurIPS 2024
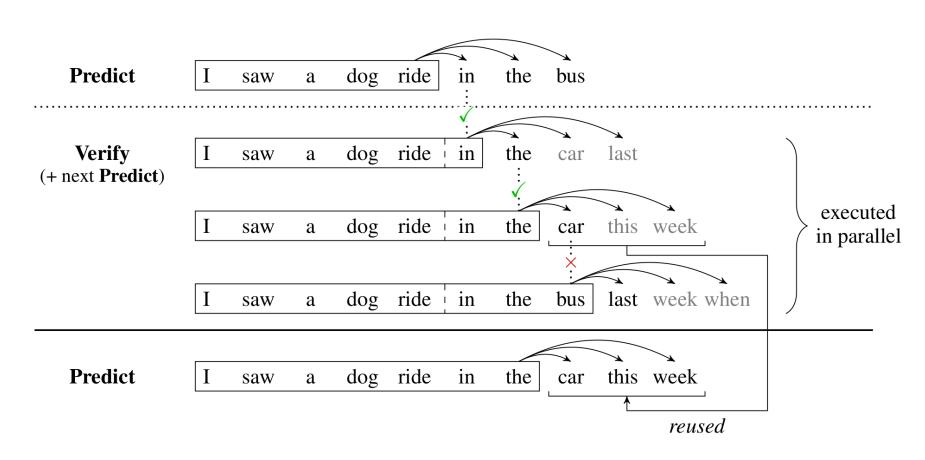
Accelerated Generation Techniques in LLMs
In this project, we conducted a comprehensive survey of techniques for accelerating text generation in large language models, motivated by the need to reduce inference latency in real-time and interactive applications where autoregressive decoding poses a fundamental bottleneck. With the goal of understanding how recent methods address these limitations without substantially sacrificing generation quality, I organized existing approaches into three primary categories: speculative decoding, early exiting mechanisms, and non-autoregressive generation, and analyzed their underlying principles, trade-offs, and limitations.
A Comprehensive Survey of Accelerated Generation Techniques in Large Language Models
Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Vinija Jain, Mingye Gao, Malavika Srikanth, Aman Chadha
A Comprehensive Survey of Accelerated Generation Techniques in Large Language Models
Mahsa Khoshnoodi, Vinija Jain, Mingye Gao, Malavika Srikanth, Aman Chadha
Stock market prediction
In this project, we utilized sequence learning methodologies, specifically employing Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. The goal was to generate accurate predictions that go beyond simple stock price forecasting. The project aimed to provide in-depth insights into market trends, volatility patterns, and potential price movements. The focus was on developing a predictive model that not only anticipates stock prices but also offers a comprehensive understanding of the underlying factors influencing market behavior. This broader perspective aimed to empower stakeholders with valuable information for strategic decision-making in the dynamic stock market environment. Additionally, I incorporated Transformers, implementing a time embedding layer for further refinement in the predictive capabilities.
Anomaly detection in financial behavior
In the Anomaly Detection in the Banking domain project, we developed a model based on Instance-based learning. The model utilizes user behavior analytics to detect fraudulent activities and insider threats by focusing on anomalies in user actions, such as identifying unusual logins and irregular transaction amounts. Through the incorporation of Active Learning, the model dynamically learns the system's behavior over time with an adaptive learning factor.
Recognizing the inherent challenge of achieving 100% accuracy in anomaly detection, the project adopted Ensemble Learning. This involved running multiple model instances concurrently to address false positives and negatives. The strategic approach, approved by Bank Melli Iran, the largest Iranian Bank, successfully delivered real-time anomaly detection capabilities, leading to substantial cost savings and reinforcing the bank's security and risk management protocols.
Recognizing the inherent challenge of achieving 100% accuracy in anomaly detection, the project adopted Ensemble Learning. This involved running multiple model instances concurrently to address false positives and negatives. The strategic approach, approved by Bank Melli Iran, the largest Iranian Bank, successfully delivered real-time anomaly detection capabilities, leading to substantial cost savings and reinforcing the bank's security and risk management protocols.
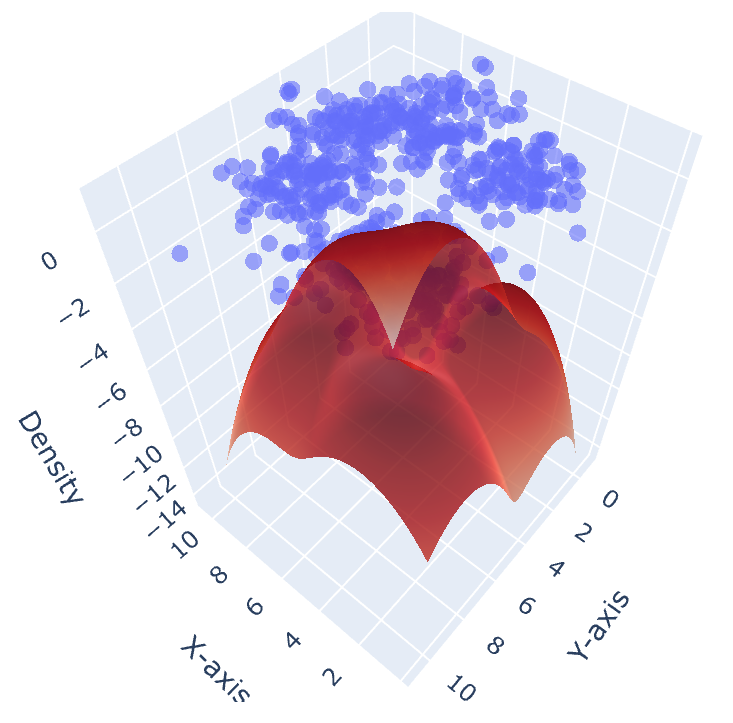
GMM for customer behaviour
In this project, an innovative approach to customer behavior analysis in commercial banking was implemented through the development of a Hierarchical Clustering model based on Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs). This advanced technique, executed using Scala within a Spark Dataframe, enabled a comprehensive understanding of complex patterns within large-scale customer datasets.
The application of GMMs in the hierarchical clustering model yielded outstanding results by revealing intricate nuances in customer behavior. The model successfully identified subtle patterns and interactions, allowing for the nuanced segmentation of clientele based on diverse banking behaviors. This in-depth analysis provided rich insights, empowering the bank to implement more targeted and personalized strategies, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and refining service offerings.
The application of GMMs in the hierarchical clustering model yielded outstanding results by revealing intricate nuances in customer behavior. The model successfully identified subtle patterns and interactions, allowing for the nuanced segmentation of clientele based on diverse banking behaviors. This in-depth analysis provided rich insights, empowering the bank to implement more targeted and personalized strategies, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and refining service offerings.
Baysian Network
In this work, an Anomaly Detection Engine was carefully designed and developed, employing Bayesian networks and Hidden Markov Models (HMM) to uncover subtle patterns and anomalies within intricate datasets. The primary objective was to create a robust model capable of identifying deviations from expected behavior, especially in scenarios where traditional methods might fall short.
The implementation of the proposed model was carried out in Java, encompassing the entire data processing pipeline. This involved rigorous data preprocessing, algorithm development, and seamless integration into the existing data pipeline. The comprehensive coverage ensured a holistic approach to anomaly detection, addressing the intricacies of diverse datasets.
To guarantee both efficiency and accuracy in anomaly detection, the project underwent thorough testing and optimization phases. These efforts were crucial in enhancing the overall quality of the data analysis process, resulting in a reliable Anomaly Detection Engine capable of handling complex datasets with precision.
The implementation of the proposed model was carried out in Java, encompassing the entire data processing pipeline. This involved rigorous data preprocessing, algorithm development, and seamless integration into the existing data pipeline. The comprehensive coverage ensured a holistic approach to anomaly detection, addressing the intricacies of diverse datasets.
To guarantee both efficiency and accuracy in anomaly detection, the project underwent thorough testing and optimization phases. These efforts were crucial in enhancing the overall quality of the data analysis process, resulting in a reliable Anomaly Detection Engine capable of handling complex datasets with precision.
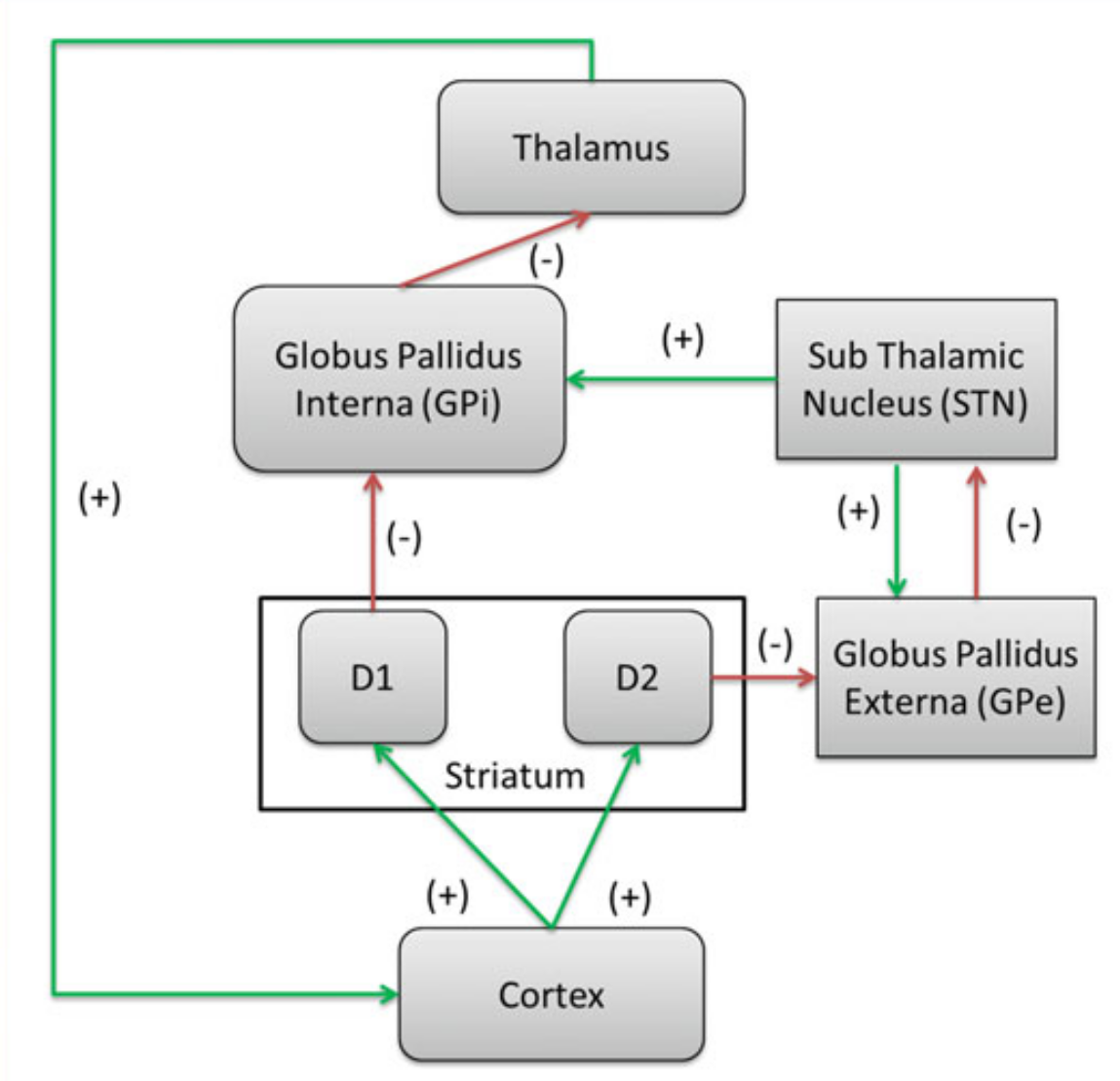
Human brain modeling
In my master's thesis, the focus was on computatiola models of human brain inspired by physiological findings, particularly the Basal Ganglia. The primary objective was to advance computational models of the Basal Ganglia, a vital group of subcortical nuclei integral to decision-making and planning tasks. The research introduced a comprehensive computational model for action selection and the sequence learning, aligning with physiological findings related to the Basal Ganglia. The model featured two distinct neural networks inspired by this brain structure. The first, a Fuzzy neural network, employed Reinforcement Learning to generate action sequences, mirroring the direct pathways of the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. The second part of the model focused on a recurrent neural network designed to automatically reproduce action sequences, drawing inspiration from the basal ganglia's neurological mechanisms.
The project's novelty lay in the development and assessment of these computational models, where the fuzzy neural network demonstrated efficiency in common reinforcement learning problems, and the recurrent neural network showcased notable capacity in the automatic reproduction of action sequences. The research aimed to contribute valuable insights into the computational understanding of the Basal Ganglia and its role in cognitive processes.
The project's novelty lay in the development and assessment of these computational models, where the fuzzy neural network demonstrated efficiency in common reinforcement learning problems, and the recurrent neural network showcased notable capacity in the automatic reproduction of action sequences. The research aimed to contribute valuable insights into the computational understanding of the Basal Ganglia and its role in cognitive processes.
Artificial Immune system for anomaly detection
My undergraduate project involves the implementation of an Artificial Immune System for anomaly detection, specifically focusing on utilizing negative selection algorithms to identify anomalies in web attacks. By mimicking the principles of the human immune system, the model employs negative selection to distinguish between normal and potentially harmful patterns in web traffic. This innovative approach contributes to the enhancement of digital security measures by providing a robust mechanism for detecting anomalies indicative of web attacks.